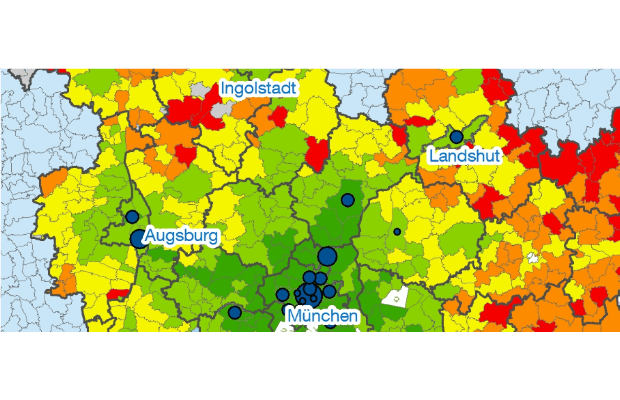
The TUM Accessibility Atlas is a multi-modal GIS-based instrument specifically developed for decision-making in the Munich Metropolitan Region. Hence, thematic datasets and measures (e.g. ... More
The TUM Accessibility Atlas is a multi-modal GIS-based instrument specifically developed for decision-making in the Munich Metropolitan Region. Hence, thematic datasets and measures (e.g. monetary costs, carbon emissions) were added to ensuring the ability to tackle the latest planning issues. The accessibility analysis ranges from regional (e.g. car and public transport) to local neighborhood scale taking into account active mobility (walking and cycling). The aim is to create a suitable instrument which can be used by a wide range of stakeholders (e.g. practitioners, decision-makers, citizens) raising awareness of the implications of their actions (e.g. land-use and transport interventions or individual mobility behavior).
Less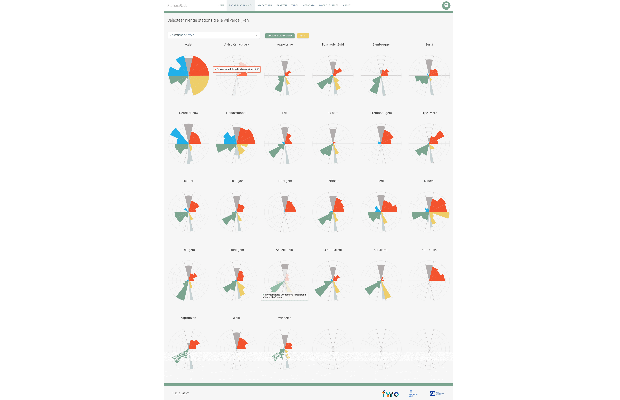
StationsRadar is an open web-based planning support tool intended to support integrated land use and transport strategy-making, with a geographical focus on railway stations and their area... More
StationsRadar is an open web-based planning support tool intended to support integrated land use and transport strategy-making, with a geographical focus on railway stations and their areas in the regions of Flanders and Brussels. The main feature of the tool is that it allows to visualize accessibility profiles for selections of stations that are made by the user. Besides these profiles, additional graphs, maps and information can be consulted. The tool was validated in the Flemish planning practice and aims to support policy and planning discussions dealing with the development potential of railway stations and their areas in Flanders and Brussels.
Less
GOAT stands for Geo Open Accessibility Tool. This web-instrument is meant to be open source, interactive, flexible and useful for accessibility planning. It is developed by Plan4Better Gmb... More
GOAT stands for Geo Open Accessibility Tool. This web-instrument is meant to be open source, interactive, flexible and useful for accessibility planning. It is developed by Plan4Better GmbH. GOAT is designed to model active mobility (e.g. walking, cycling), enhancements and extensions (e.g. public transport) are done on a regular basis. Plan4Better provides the tool as software-as-a-service worldwide and you can test the demo version for the City of Munich.
Less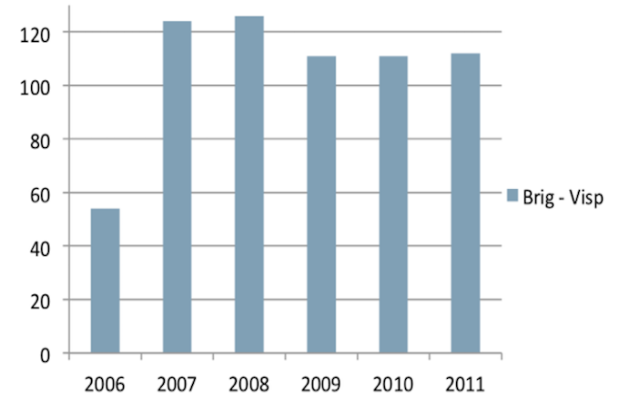
The instrument measures different types of accessibility. First travel times between municipalities are measured. Also these travel times are compared over years to have an overall view. A... More
The instrument measures different types of accessibility. First travel times between municipalities are measured. Also these travel times are compared over years to have an overall view. Accessibility in this case means not only the time needed and distance to a newly developed transport infrastructure. The instrument looks also on accessibility aspects before and after the new transport infrastructure was established in the same municipality. Also it has a stronger look on regions which are no longer connected, because of the new transport infrastructure, traversing another way. The instrument is most useful after implementing a new transport infrastructure, because it is hard to analysis social behaviour before something happened in reality
Less
This Manual is a guide for quantifying and evaluating access for anybody interested in truly understanding how to measure the performance of transport and land use configurations. It conta... More
This Manual is a guide for quantifying and evaluating access for anybody interested in truly understanding how to measure the performance of transport and land use configurations. It contains enough to help transport and planning professionals achieve a more comprehensive look at their city or region than traditional transport analysis allows. It provides a point of entry for interested members of the public as well as practitioners by being organized in a logical and straightforward way. Date 2020-01-01 Publisher Committee of the Transport Access Manual, University of Sydney Licence Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0.
Less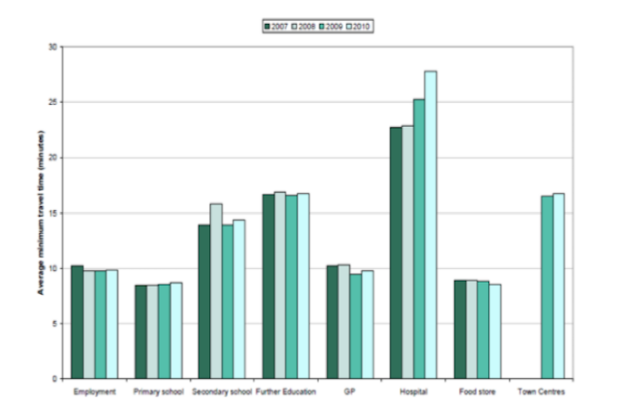
The basic concepts in ACCALC are that it is a relational database helping planners to manage large and complex data sets and to output meaningful accessibility indicators (DfT 2011). Versi... More
The basic concepts in ACCALC are that it is a relational database helping planners to manage large and complex data sets and to output meaningful accessibility indicators (DfT 2011). Version 1 allowed users to upload spatially referenced data on land uses, spatially referenced data on locations from which trips are generated and tables showing the deterrents affecting travel between each origin and destination location. Functions are provided to automate the calculation of a variety of common accessibility indicators formulations. In general users concentrate on travel time analysis since the data is more readily available. However analysis of travel costs is also common.
Less
What opportunities for social cohesion do cities provide? Is your neighbourhood park frequented by a homogenous or diverse mix of people? How many amenities can you reach within a short wa... More
What opportunities for social cohesion do cities provide? Is your neighbourhood park frequented by a homogenous or diverse mix of people? How many amenities can you reach within a short walking distance? And do you often encounter people from different walks of life? The interactive CTwalk web tool maps opportunities that different age groups can reach in a 5 or 15-minute walk. It uses granular population, location, and pedestrian network data from open sources to estimate how many children, adults, and elderly citizens can reach various destinations in a city within a short walk. By emphasizing the degree of pedestrian co-accessibility of various city destinations, CTwalk Map seeks to highlight the social cohesion potential of neighbourhoods while also unmasking local access inequities.
Less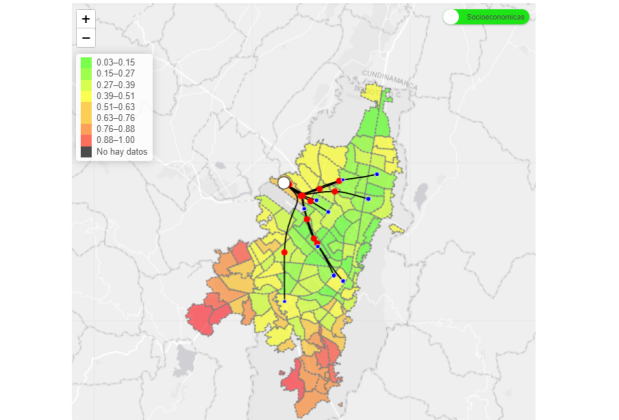
VulnerApp is a public transport data viewer for Bogota and Soacha, the values are estimated using information from the Bogota Mobility Survey 2019, in which you can explore a set of mobili... More
VulnerApp is a public transport data viewer for Bogota and Soacha, the values are estimated using information from the Bogota Mobility Survey 2019, in which you can explore a set of mobility variables and their distribution by UTAM (Territorial Unit of Mobility Analysis), in the same way, there are several filters associated with socioeconomic factors of its inhabitants. Additionally, you can view the accessibility index calculated for each function of the city, using mobility variables like travel time, waiting and walking time, transferences, and others, as well as the main destinations associated with each reason for travel according to the UTAM of origin, and consult the coverage of public transport fare subsidies.
Less
accessibility offers a set of fast and convenient functions to calculate multiple transport accessibility measures. Given a pre-computed travel cost matrix and a land use dataset (containi... More
accessibility offers a set of fast and convenient functions to calculate multiple transport accessibility measures. Given a pre-computed travel cost matrix and a land use dataset (containing the location of jobs, healthcare and population, for example), the package allows one to calculate active and passive accessibility levels using multiple accessibility measures, such as: cumulative opportunities (using either travel cost cutoffs or intervals), minimum travel cost to closest N number of activities, gravity-based (with different decay functions) and different floating catchment area methods.
Less
r5r is an R package for rapid realistic routing on multimodal transport networks (walk, bike, public transport and car). It provides a simple and friendly interface to R5, the Rapid Realis... More
r5r is an R package for rapid realistic routing on multimodal transport networks (walk, bike, public transport and car). It provides a simple and friendly interface to R5, the Rapid Realistic Routing on Real-world and Reimagined networks, the routing engine developed independently by Conveyal. r5r is a simple way to run R5 locally, allowing R users to generate detailed routing analysis or calculate travel time matrices and accessibility using seamless parallel computing.
Less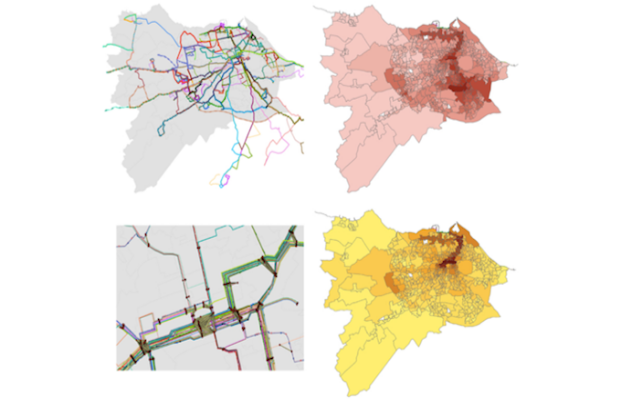
Spatial Network Analysis of Public Transport Accessibility (SNAPTA) is a GIS - based accessibility instrument that relies on a package of different measures to quantify spatial accessibili... More
Spatial Network Analysis of Public Transport Accessibility (SNAPTA) is a GIS - based accessibility instrument that relies on a package of different measures to quantify spatial accessibility to urban services and activity opportunities by public transport modes. The instrument, therefore, takes into account the land use and transport characteristics of urban interactions and the availability of opportunities that can be accessed by public transport. It focuses on groups of people, and their social and economic activity needs to be met at different destinations. It assumes that travel demand will be determined by the attractiveness of these locations and the quality of the transport infrastructure linking these places.
Less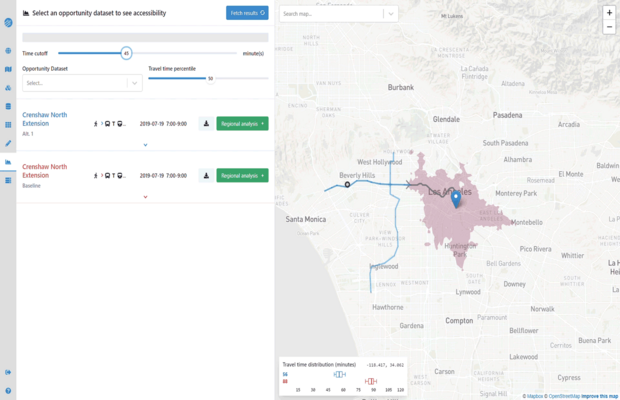
Conveyal is a web-based tool that enables users to create detailed scenarios, then rapidly evaluate them in terms of accessibility. It automatically builds multi-modal networks for metropo... More
Conveyal is a web-based tool that enables users to create detailed scenarios, then rapidly evaluate them in terms of accessibility. It automatically builds multi-modal networks for metropolitan regions, through uploaded street network (OSM), transit feed (GTFS), and other geospatial data. Conveyal’s innovative methods provide unique insights into temporal variation. For example, users can edit transit frequency levels with the built-in scenario editor, then compare impacts at different percentiles of travel time. Running in the cloud, Conveyal scales to provide results in seconds, even for billions of origin-destination pairs. Transport departments and planning authorities have used Conveyal to evaluate city, state, and national scenarios in more than 30 countries around the world.
Less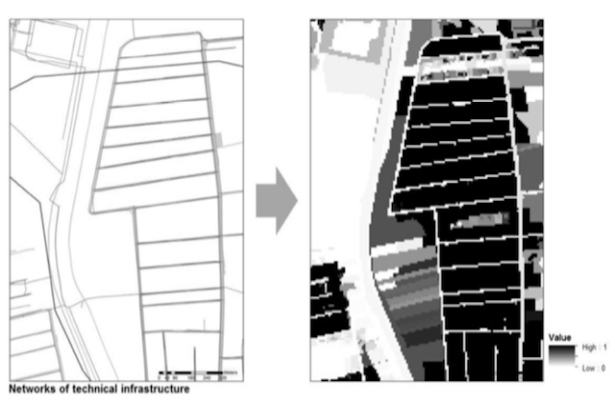
The proposed instrument defines the accessibility to technical infrastructure at the strategic level of spatial planning. Accessibility to technical infrastructure is in the first stage de... More
The proposed instrument defines the accessibility to technical infrastructure at the strategic level of spatial planning. Accessibility to technical infrastructure is in the first stage defined in terms of the physical accessibility to the technical infrastructure. Physical accessibility to technical infrastructure is measured as the accessibility to the provided land use at the local level, taking into account the capacity of the existing and planned technical infrastructure and the physical distance from the technical infrastructure. However, the final goal of the instrument is to define the cost accessibility to the technical infrastructure as well.
Less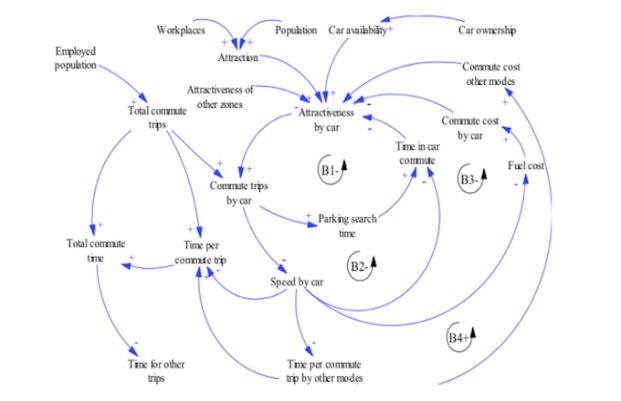
The main innovation in MARS is that the different reaction speeds of the two systems (passenger transport system and land use system) are taken into consideration. These different speeds g... More
The main innovation in MARS is that the different reaction speeds of the two systems (passenger transport system and land use system) are taken into consideration. These different speeds generate a dynamic process which is looking for a dynamic equilibrium, which is disturbed by external transport or land use policy measures, such as road capacity increases, public transport supply changes or land use instruments, such as e.g. a land value capture tax. MARS calculates the accessibility for each zone for each means of transport for each simulation period and uses this information to redistribute the daily trips of population as well as the relocation of workplaces and housing within the case study area for a simulation period of 30 years.
Less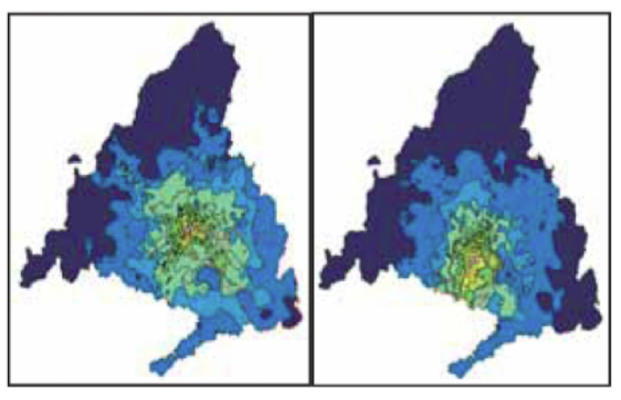
One of the main motivations of the IMaFa accessibility instrument is to assess the level of service of public transport when accessing shopping centres in the MetroSur influence area. Howe... More
One of the main motivations of the IMaFa accessibility instrument is to assess the level of service of public transport when accessing shopping centres in the MetroSur influence area. However isochrone maps can be applied to other type of facilities (health care, education, etc.). The instrument of isochrone maps defines accessibility as the opportunities for ease of access and takes as a case study the access to shopping centres by public transit. The accessibility instrument is measured as the process associated with getting to and from the shopping centres by public transit. The main strengths of the present accessibility instrument are its low data requirements, and the ease of calculation, transmission and interpretation of results.
Less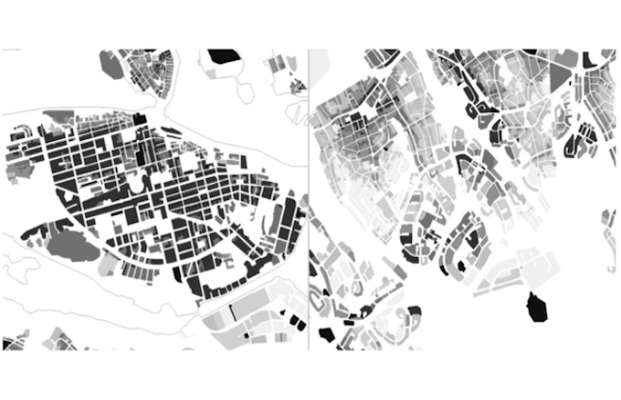
Place Syntax Tool (PST) is an application for the desktop software MapInfo. Place syntax introduces the possibility to conduct descriptions and analyses of accessibility from a life-world... More
Place Syntax Tool (PST) is an application for the desktop software MapInfo. Place syntax introduces the possibility to conduct descriptions and analyses of accessibility from a life-world point of view in just as systematic and quantitative a way. The ‘place syntax’ approach has great potential for the development of new tools for urban planning and design, not only for predicting pedestrian flow or estimating urban accessibilities, not least to redefine the concepts of densities and areas. The aim of the research is to help urban studies and practice to find new and possibly more informative ways or presenting place data in general.
Less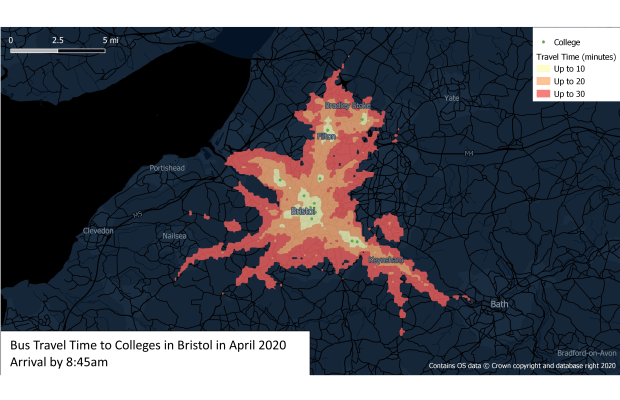
A multi-modal travel accessibility tool that allows editing of network data to produce what-if scenarios and utilises detailed demographic data. Over 500 users worldwide from local to cent... More
A multi-modal travel accessibility tool that allows editing of network data to produce what-if scenarios and utilises detailed demographic data. Over 500 users worldwide from local to central/federal governments, healthcare and private industry, TRACC has been used to identify key locations for housing, healthcare, transport routes and is used to inform policy. TRACC allows calculations at both local and national level and is commonly used for local government to create accessibility/local plans to inform which areas of a region have poor access and where investment is required.
Less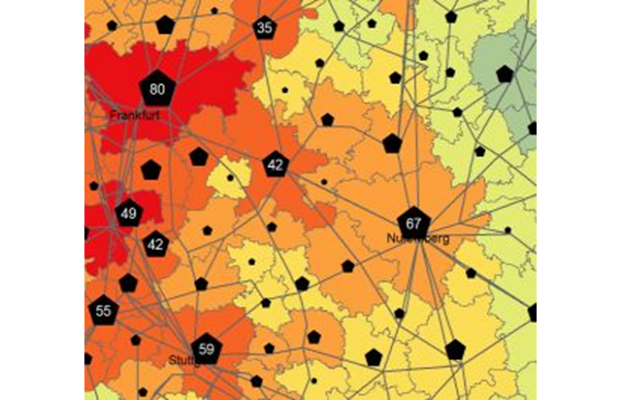
The European Rail Accessibility Model developed at the Chair of Urban Development, Technical University of Munich tracks and projects changes of accessibility induced by the development of... More
The European Rail Accessibility Model developed at the Chair of Urban Development, Technical University of Munich tracks and projects changes of accessibility induced by the development of high-speed rail since 1990 and until 2030. It monitors gravitational accessibility of population as well as a number of graph theory-based connectivity measures (such as degree and betweenness centrality) on a regional scale.
Less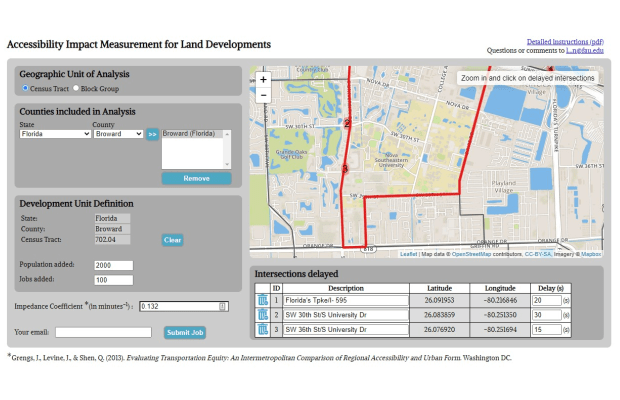
This tool is intended for the accessibility-based evaluation of specific transportation and land-use projects. For land-use projects, a population and employment increase must be associate... More
This tool is intended for the accessibility-based evaluation of specific transportation and land-use projects. For land-use projects, a population and employment increase must be associated with the project along with intersection-specific travel time delays. Then the change in auto-based accessibility to jobs is calculated. For transportation projects, land-use and transportation patterns before the project are compared with land-use and transportation patterns after the project, with a comparison for the average per capita job accessibility provided.
Less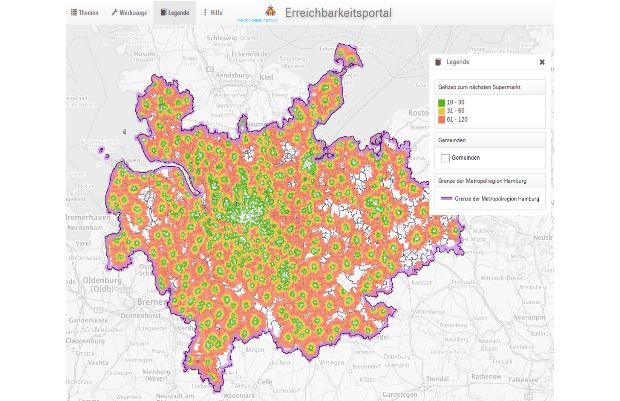
A publicly available web page that includes around 200 accessibility indicators in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region (100-meter and 500-meter grid). The analyses consists of distance, cumula... More
A publicly available web page that includes around 200 accessibility indicators in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region (100-meter and 500-meter grid). The analyses consists of distance, cumulative as well as potential measures for all modes of transport. The web instrument also includes 25 different types of destinations including schools, supermarkets and jobs. What can you do?
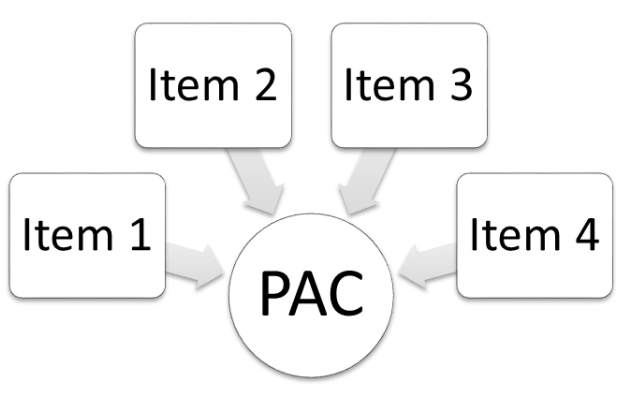
The PAC is a psychometric scale which evaluates the individuals´own perceptions of accessibility either for daily travel in general, or by a specific transport mode or combinations of mode... More
The PAC is a psychometric scale which evaluates the individuals´own perceptions of accessibility either for daily travel in general, or by a specific transport mode or combinations of modes. The PAC was developed by researchers at Karlstad University, Sweden, as a complement to objectively based accessibility tools and focus lies on capturing the individual dimension of accessibility. The PAC has been used in practice in a number of countries and may be helpful in identifying segments of individuals (or areas) with low accessibility, or to evaluate effects of different interventions from the perspective of the travelers. It comes in three versions, each consisting of 4 items (scale 1-7) which may be assessed separately or together as an index for an overall perceived accessibility score.
Less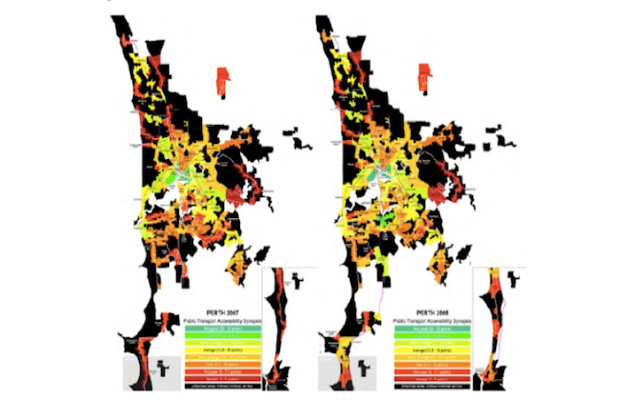
SNAMUTS is a GIS-based tool to assess the relationship between public transport network configuration, performance and service standards on the one hand, and the geographical distribution ... More
SNAMUTS is a GIS-based tool to assess the relationship between public transport network configuration, performance and service standards on the one hand, and the geographical distribution or clustering of land use activities across a metropolitan area on the other hand. The instrument breaks down the land use-transport system into a set of activity nodes and route segments derived from the hierarchy of activity centres identified in strategic planning documents, and the location and service standard of public transport routes.
Less
TRACE - Retail Cluster Accessibility was designed to analyse the retail landscape of Flanders and as a possible aid for developing a new restrictive retail policy based on spatial planning... More
TRACE - Retail Cluster Accessibility was designed to analyse the retail landscape of Flanders and as a possible aid for developing a new restrictive retail policy based on spatial planning. The tool tests to what extent the parameters of the classic spatial interaction models are still valuable. TRACE is able to show which areas are interesting for retailers to invest in, areas where they can fulfil their economic needs, by linking clusters to socioeconomic location factors. The tool has been developed using Model Builder in the ArcGIS 10 suit, developed and distributed by ESRI.
Less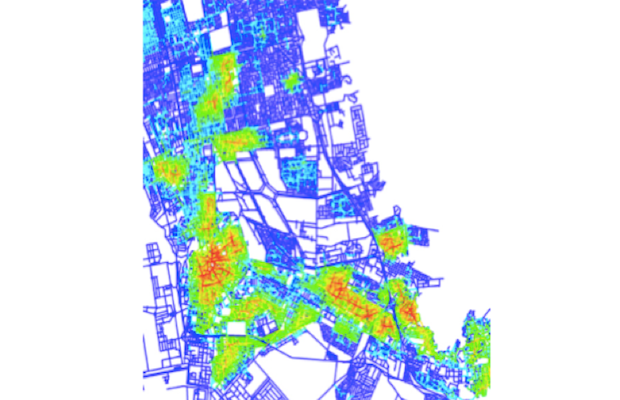
The instruments presented here are: Spatial Integration Accessibility (SIA) and Angular Segment Analysis by Metric Distance (ASAMD) and they both belong to the wider theoretical and method... More
The instruments presented here are: Spatial Integration Accessibility (SIA) and Angular Segment Analysis by Metric Distance (ASAMD) and they both belong to the wider theoretical and methodological field of space syntax developed in the Space Lab of University College London. Both instruments are measuring spatial accessibility. SIA is using a spatial representation called axial line and on the topological distance between axial lines based on the number of steps from one line to the other while ASAMD includes in the axial analysis furthermore the angles of incidence between lines, the segmentation by junction of the axial line and the effect that metric radii would have on the choice of routes and the trips destinations.
Less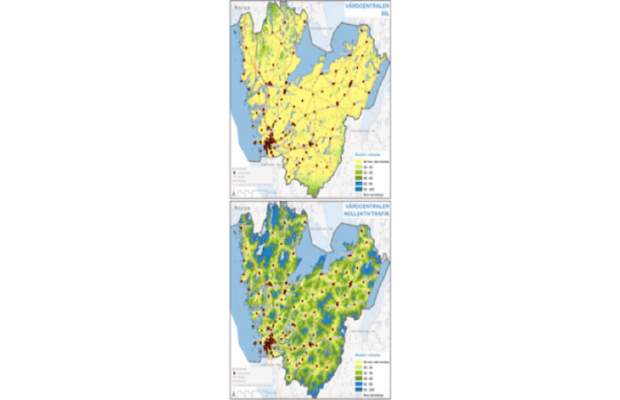
The instrument calculates travel time for car and public transport to one or many selected destinations with a 500 m geographical resolution for the entire Västra Götaland region. It is ... More
The instrument calculates travel time for car and public transport to one or many selected destinations with a 500 m geographical resolution for the entire Västra Götaland region. It is also spatially compatible with a large number of socio-economic data sets, which enables further analysis. The core of the calculation and data manipulation is developed by a consultancy firm3 as a plug-in using the TransCAD software package. For further analysis and visualisation other GIS software is used. Public transport travel time calculations are based on time table OD data.
Less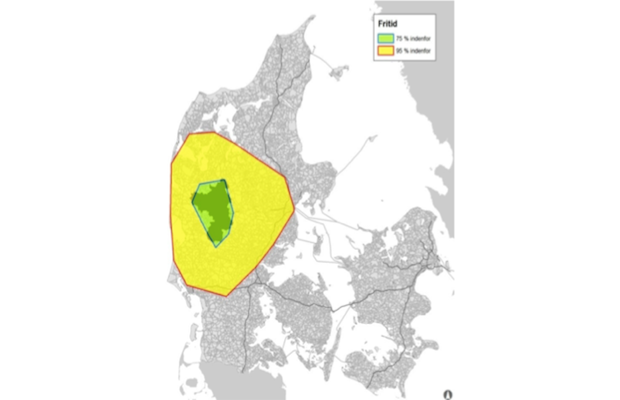
This instrument may be applied purposefully in planning as well as in scientific context. Representing ‘actual’ behaviours can supplement and provide a basis for interpretation accessibili... More
This instrument may be applied purposefully in planning as well as in scientific context. Representing ‘actual’ behaviours can supplement and provide a basis for interpretation accessibility and access needs. The main strength of this instrument is that it may be said to represent what people do. On this basis it may gain acceptance and wide application and allow for multiple interpretations.
Less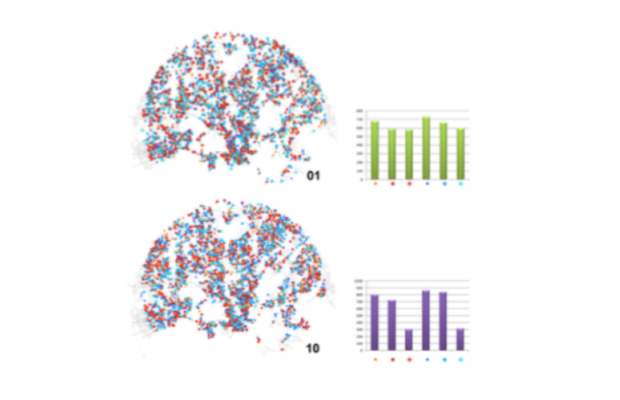
The model HIMMELI consists of two major modules: (1) an initialisation module and (2) a simulation module. The initialisation module includes all functions that read all the input data for... More
The model HIMMELI consists of two major modules: (1) an initialisation module and (2) a simulation module. The initialisation module includes all functions that read all the input data for the model. The input data includes information concerning households, retail services and transportation system. The actual processing of the data then happens in the simulation module which runs the given number of simulation cycles. The idea is to model the cumulative effects of accessibility and the interaction of urban actors within the physical framework created by the urban structures. The focus of the modelling tool is to observe how different accessibility factors influence on a spatial organization of retail units and how this process can be simulated by using agent based modelling methodologies.
Less
Spatiality_lines aims at contributing a way of measuring how a street grid becomes metrically denser or sparser, more or less intelligible and more or less easily accessible. One practical... More
Spatiality_lines aims at contributing a way of measuring how a street grid becomes metrically denser or sparser, more or less intelligible and more or less easily accessible. One practical outcome is to support the appropriate design of streets as part of urban developments. It can inform us on how the street network can be designed so as to ensure that some places, intended as retail hubs, business cores or local centres, will be more likely to attract higher densities of movement, whereas others, intended for residential uses, will remain quieter (Hillier, 1993).
Less
The instrument developed by SiTI, called InViTo (acronym of Interactive Visualization Tool), aims to provide a visual interactive support to large scale planning processes. The tool is int... More
The instrument developed by SiTI, called InViTo (acronym of Interactive Visualization Tool), aims to provide a visual interactive support to large scale planning processes. The tool is intended to provide an effective basis for sharing information and enabling discussion among different actors such as planners, stakeholders and, in general, non-expert people within focus groups, workshops, participative and collaborative processes. The main strength of InViTo is represented by the possibility of managing interactive and dynamic scenarios, in order to visualize in real time the effects of decision making on urban form and to support the planning processes.
Less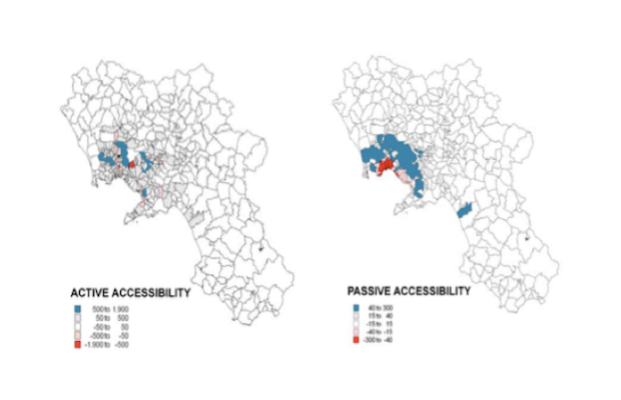
The accessibility instrument GraBAM (Gravity-Based Accessibility Measures) can be used to answer the following planning question: ‘Who reaps the benefits from investments in the transport ... More
The accessibility instrument GraBAM (Gravity-Based Accessibility Measures) can be used to answer the following planning question: ‘Who reaps the benefits from investments in the transport system, and where are these benefits localised?’ It can be applied in a variety of operational planning and public involvement activities of transport agencies. The tool can identify the interrelations between transport infrastructures (changing zonal accessibility) and the spatial distribution of the impacts on socio-economic activities. GraBAM can also assist urban planners in identifying optimal locations for new development areas. Moreover, it can also support the analysis of the real estate market dynamics.
Less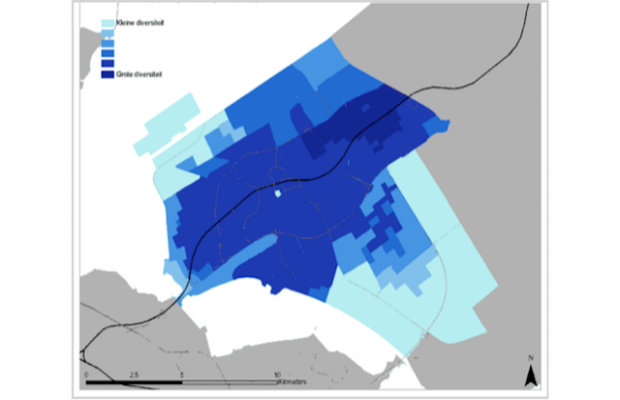
The Joint Accessibility Design framework consists of a methodology that uses accessibility mapping to enhance coherent decision-making between urban and mobility planning. Accessibility ma... More
The Joint Accessibility Design framework consists of a methodology that uses accessibility mapping to enhance coherent decision-making between urban and mobility planning. Accessibility maps depict the accessibility of specific locations within a city or region, considering one or more specific modes of transportation, time of day and target group. The JAD framework provides planners with the possibility to understand interdependencies between transport and land-use development, and thus support the exploration of the scope for joint action.
Less
This instrument has been developed by the planning authorities in Oslo, in order to help dimension shopping centres in the municipality in accordance with their overall plan for developmen... More
This instrument has been developed by the planning authorities in Oslo, in order to help dimension shopping centres in the municipality in accordance with their overall plan for development of shopping and services (Municipality of Oslo, 2003). The planning authorities apply the method, together with the plan itself, to calculate the maximum size for new shopping centres or extensions of shopping centres in specific locations, in order for the centre to serve a population about equal to the number living in walking- and bicycling distance from the centre. The instrument and the plan are interrelated.
Less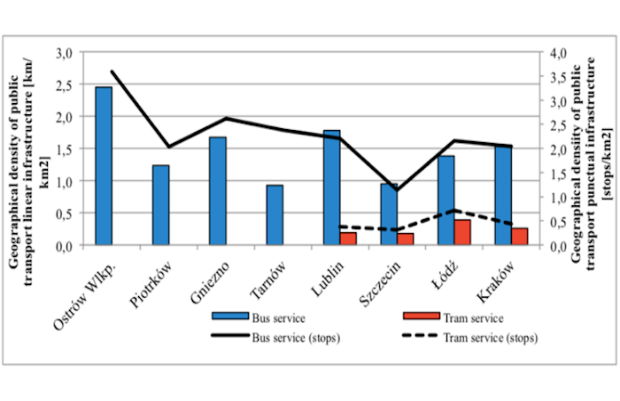
The Geographic/Demographic Accessibility of Transport Infrastructure GDATI instrument assesses the public transport system in relation to its features (such as number of stops, length of r... More
The Geographic/Demographic Accessibility of Transport Infrastructure GDATI instrument assesses the public transport system in relation to its features (such as number of stops, length of routes), and to the area where it operates and the number of inhabitants that should be served by this system. The accessibility measure is assessed based on the previously recorded demographic and geographic indicators of settings and public transport operation factors.
Less
The SAL tool is a geographical representation of comparative accessibility levels by types of transport modes to different types of opportunities generating travel. It is based on the conc... More
The SAL tool is a geographical representation of comparative accessibility levels by types of transport modes to different types of opportunities generating travel. It is based on the concept of accessibility, defined as the extent to which the land use and transport systems enable individuals to reach different types of opportunities. More specifically, SAL proposes the concept of ‘structural accessibility’ for assessing how urban structures constrain travel choices. In other words, it provides foresight on how specific land use and transport policies enable or limit particular choices of the inhabitants.
Less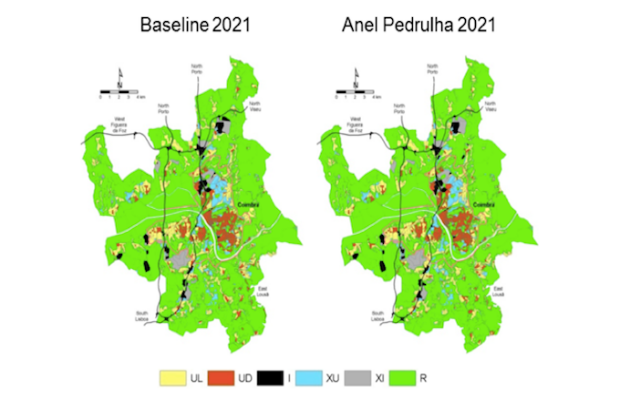
UrbCA is a dynamic model that simulates land use change over a space divided into irregular cells designed from the traditional census blocks. Cells have at each moment a given cell state ... More
UrbCA is a dynamic model that simulates land use change over a space divided into irregular cells designed from the traditional census blocks. Cells have at each moment a given cell state (or land use) from a finite cell of cell states which change through time taking into account the cell states of a given number of neighboring cells. This evolution is provided by a set of transition rules that parameterize the behaviors of all the drivers at stake. The use of UrbCA in the appraisal of accessibility in planning focuses on the possibility of simulating different planning solutions under different planning parameters taking into account different accessibility conditions, which are a result of the investments on the road network.
Less